import numpy as np
from pwtools import num, pwscf, common, mpl
[docs]
def kpath(vecs, N=10):
"""Simple k-path. Given a set of K vectors (special points in the BZ),
generate a "fine path" of N*(K-1)+1 vectors along the path defined by the
vectors in `vecs`. The K vectors are the "vertices" of the k-path and we
construct the fine path by connecting the vertices by their distance
vectors and placing N points on each connection edge.
Parameters
----------
vecs : array (K,M)
Array with K vectors of the Brillouin zone (so M = 3 usually :)
N : int
Returns
-------
new_vecs : array (N*(K-1)+1,M)
Array with a fine grid of vectors along the path
defined by `vecs`.
Notes
-----
This is the simplest method one can think of. Points on the "fine path" are
not equally distributed. The distance between 2 vertices (k-points) doesn't
matter, you will always get N points between them. For a smooth dispersion
plot, you need N=20 or more.
"""
K = vecs.shape[0]
new_vecs = np.empty(((K-1)*N+1, vecs.shape[1]), dtype=float)
for i in range(1, K):
new_vecs[(i-1)*N:i*N, :] = num.vlinspace(vecs[i-1,:], vecs[i,:], N,
endpoint=False)
new_vecs[-1,:] = vecs[-1,:]
return new_vecs
[docs]
def get_path_norm(ks):
"""Like in QE's ``plotband.f90``, path_norm = kx there. Return a sequence of
cumulative norms of the difference vectors which connect each two adjacent
k-points.
Parameters
----------
ks : array (nks, 3)
array with `nks` k-points on the path
"""
dnorms = np.empty(ks.shape[0], dtype=float)
dnorms[0] = np.linalg.norm(ks[0,:])
# diff(...): array with difference vecs, norm of each of them
dnorms[1:] = np.sqrt((np.diff(ks, axis=0)**2.0).sum(axis=1))
# cumulative sum
path_norm = dnorms.cumsum(axis=0)
return path_norm
[docs]
class SpecialPointsPath:
r"""Sequence of special points. Calculate their path norm and store symbols
such as "K" or "$\\Gamma$"."""
[docs]
def __init__(self, ks=None, ks_frac=None, symbols=None):
"""
Parameters
----------
ks : (nks,3)
cartesian k-points
ks_frac : (nks,3), optional
fractional k-points, used only in :func:`plot_dis`, not for path
norm calculation
symbols : sequence of strings (nks,), optional
special point symbol each point in `ks`
"""
assert (ks is not None) and (ks_frac is not None), ("use either ks or ks_frac")
self.ks = ks
self.ks_frac = ks_frac
self.symbols = symbols
# 1d array (nks,) of cumulative norms
self.path_norm = get_path_norm(self.ks)
[docs]
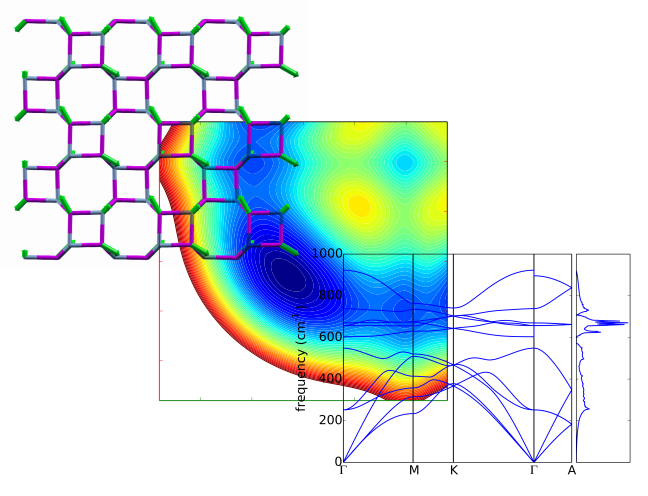
def plot_dis(path_norm, freqs, special_points_path=None,
show_coords=None, dos=None, ax=None, ylim=None, **kwargs):
"""Plot dispersion.
See ``bin/plot_dispersion.py`` for a usage example. This lives here (and not in
:mod:`~pwtools.pwscf`) b/c it is not PWscf-specific. It can be used for any
dispersion data (band structure).
See :func:`~pwtools.pwscf.read_matdyn_freq` for how to get `freqs` in the
case of phonon dispersions.
This function is a convenience function, which can even plot the DOS as
well. We do not expose many matplotlib parameters here. If you want to tweak
your plot much, then operate on the returned `fig`, `ax` (dispersion) and
`axdos` (dos), or copy and hack the function, which might be actually the easiest
way.
Parameters
----------
path_norm : array (nks,)
x-axis with cumulative norms of points along the k-path, see
:func:`get_path_norm`
freqs : array (nks, nbnd)
`nbnd` frequencies for each band at each k-point
special_points_path : optional, :class:`SpecialPointsPath` instance
used for pretty-printing the x-axis (set special point labels)
show_coords : 'cart', 'frac', None
Show the cartesian or fractional coordinates of special points in the
x-axis label, on neither if None.
dos : array (N,2) or None
array with phonon dos to plot: ``dos[:,0]=freq``, ``dos[:,1]=phdos``
ax : matplotlib AxesSubplot (e.g. from ``fig,ax=pwtools.mpl.fig_ax()``)
automatically created if None
ylim : tuple (2,)
frequency axis limits
**kwargs : keywords
passed to plot()
Returns
-------
fig, ax, axdos
fig : matplotlib Figure to ax
ax : matplotlib AxesSubplot with dispersion
axdos : matplotlib AxesSubplot with dos, or None if `dos=None`
Examples
--------
>>> spp = kpath.SpecialPointsPath(ks=np.array([[0,0,0], [1.5,0,0], [2.3,0,0]]),
symbols=['A', 'B', 'C'])
>>> path_norm = np.linspace(0,2.5,100)
>>> freqs = np.random.rand(100,5)*500
>>> # create fig,ax inside, returned axdos=None
>>> fig,ax,axdos = kpath.plot_dis(path_norm, freqs, spp)
>>> # pass ax from outside, returns fig,ax but we don't use that b/c ax
>>> # is in-place modified
>>> fig,ax = mpl.fig_ax()
>>> kpath.plot_dis(path_norm, freqs, spp, ax=ax)
>>> # plot also DOS
>>> dos = np.empty((30,2)); dos[:,0]=np.linspace(0,500,30); dos[:,1]=rand(30)
>>> fig,ax,axdos = kpath.plot_dis(path_norm, freqs, spp, dos=dos)
See Also
--------
:func:`get_path_norm`
:func:`pwtools.pwscf.read_matdyn_freq`
:ref:`dispersion_example`
"""
if ax is None:
fig,ax = mpl.fig_ax()
else:
fig = ax.get_figure()
# Plot columns of `freq` against q points (path_norm)
ax.plot(path_norm, freqs, **kwargs)
if special_points_path is not None:
ylim = ax.get_ylim() if ylim is None else ylim
ks, ks_frac, nrm, symbols = \
special_points_path.ks, \
special_points_path.ks_frac, \
special_points_path.path_norm, \
special_points_path.symbols
ax.vlines(nrm, ylim[0], ylim[1])
fmtfunc = lambda x: "%.2g" %x
if show_coords is None:
labels = symbols
else:
if show_coords == 'cart':
ks_plot = ks
elif show_coords == 'frac':
ks_plot = ks_frac
else:
raise Exception("show_coords = 'cart', 'frac' or "
"None needed")
labels = ['%s\n[%s]' %(sym, common.seq2str(kk, func=fmtfunc,sep=','))\
for sym,kk in zip(symbols, ks_plot)]
ax.set_xticks(nrm)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
ax.set_xlim(path_norm[0], path_norm[-1])
ax.set_ylabel("frequency (cm$^{-1}$)")
if dos is not None:
# http://matplotlib.org/examples/axes_grid/scatter_hist.html
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1 import make_axes_locatable
divider = make_axes_locatable(ax)
axdos = divider.append_axes("right", 1.2, pad=0.1, sharey=ax)
axdos.plot(dos[:,1], dos[:,0], 'b')
mpl.plt.setp(axdos.get_yticklabels(), visible=False)
mpl.plt.setp(axdos.get_xticklabels(), visible=False)
axdos.xaxis.set_tick_params(size=0)
else:
axdos = None
return fig, ax, axdos